What Element Can Form The Most Covalent Bonds
What Element Can Form The Most Covalent Bonds - Web the chemical elements most likely to form covalent bonds are those that share electrons, such as carbon, as opposed to those that take them from another. In a covalent bond, the stability of the bond comes from the shared electrostatic attraction between the two. Web polar covalent bonds. Web lewis proposed that an atom forms enough covalent bonds to form a full (or closed) outer electron shell. The pair of electrons participating in this type of bonding is called a. A bond in which the electronegativity difference between the atoms is between 0.5 and 2.1 is called a polar covalent bond. Web the number of covalent bonds an atom can form is called the valence of the atom. Boron commonly makes only three covalent bonds, resulting in only six. The valence of a given atom is the same in most stable neutral organic compounds. Electron pairs shared between atoms of equal or very similar electronegativity constitute a nonpolar covalent bond (e.g.,. Nonmetal atoms frequently form covalent bonds with other nonmetal atoms. In a covalent bond, the stability of the bond comes from the shared electrostatic attraction between the two. Web covalent bonds involve the sharing of electron pairs between atoms. Web the number of covalent bonds an atom can form is called the valence of the atom. The valence of a. Web we would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Scientists can manipulate ionic properties and these interactions in. Web a covalent bond is formed when two atoms share electron pairs. A covalent bond is formed by the equal sharing of electrons from both participating atoms. Web a covalent bond is formed between two. Web covalent bonds involve the sharing of electron pairs between atoms. The valence of a given atom is the same in most stable neutral organic compounds. Web the most common examples are the covalent compounds of beryllium and boron. A covalent bond is formed by the equal sharing of electrons from both participating atoms. Web lewis proposed that an atom. Web a covalent bond is formed between two atoms by sharing electrons. Web a covalent bond is formed when two atoms share electron pairs. Web formation of covalent bonds. For example, beryllium can form two covalent bonds, resulting in only four electrons in its valence shell: Web covalent bonds involve the sharing of electron pairs between atoms. Web these bonds form when an electron is shared between two elements and are the strongest and most common form of chemical bond in living organisms. Web the chemical elements most likely to form covalent bonds are those that share electrons, such as carbon, as opposed to those that take them from another. The pair of electrons participating in this. Web moreover, of all the elements in the second row, carbon has the maximum number of outer shell electrons (four) capable of forming covalent bonds. The number of bonds an element forms in a covalent compound is determined by the number of electrons it. For example, the hydrogen molecule, h 2, contains a covalent bond. Web covalent bonds involve the. In the diagram of methane shown here, the carbon atom has a valence of. In a covalent bond, the stability of the bond comes from the shared electrostatic attraction between the two. This type of bonding occurs between two atoms of the same element or of elements close to each other in the. Web covalent bonds are formed between two. Web a covalent bond is formed when two atoms share electron pairs. The pair of electrons participating in this type of bonding is called a. Web formation of covalent bonds. Electron pairs shared between atoms of equal or very similar electronegativity constitute a nonpolar covalent bond (e.g.,. Web the most common examples are the covalent compounds of beryllium and boron. For example, the hydrogen molecule, h 2, contains a covalent bond. The pair of electrons participating in this type of bonding is called a. Web formation of covalent bonds. Web moreover, of all the elements in the second row, carbon has the maximum number of outer shell electrons (four) capable of forming covalent bonds. The number of bonds an element. Web formation of covalent bonds. The number of bonds an element forms in a covalent compound is determined by the number of electrons it. Nonmetal atoms frequently form covalent bonds with other nonmetal atoms. The valence of a given atom is the same in most stable neutral organic compounds. For example, beryllium can form two covalent bonds, resulting in only. A covalent bond is formed by the equal sharing of electrons from both participating atoms. In a covalent bond, the stability of the bond comes from the shared electrostatic attraction between the two. A bond in which the electronegativity difference between the atoms is between 0.5 and 2.1 is called a polar covalent bond. The number of bonds an element forms in a covalent compound is determined by the number of electrons it. Web covalent bonds are formed between two atoms when both have similar tendencies to attract electrons to themselves (i.e., when both atoms have identical or fairly similar. Web we would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. This type of bonding occurs between two atoms of the same element or of elements close to each other in the. Web the number of covalent bonds an atom can form is called the valence of the atom. Web a covalent bond is formed when two atoms share electron pairs. Web a covalent bond is formed between two atoms by sharing electrons. Web ionic bonds are important because they allow the synthesis of specific organic compounds. Web formation of covalent bonds. Web the chemical elements most likely to form covalent bonds are those that share electrons, such as carbon, as opposed to those that take them from another. Web a covalent bond is formed between two atoms by sharing electrons. Web the most common examples are the covalent compounds of beryllium and boron. Nonmetal atoms frequently form covalent bonds with other nonmetal atoms.
PPT Covalent bonding in hydrogen PowerPoint Presentation, free

covalent bond Definition, Properties, Examples, & Facts Britannica

chemistry picture
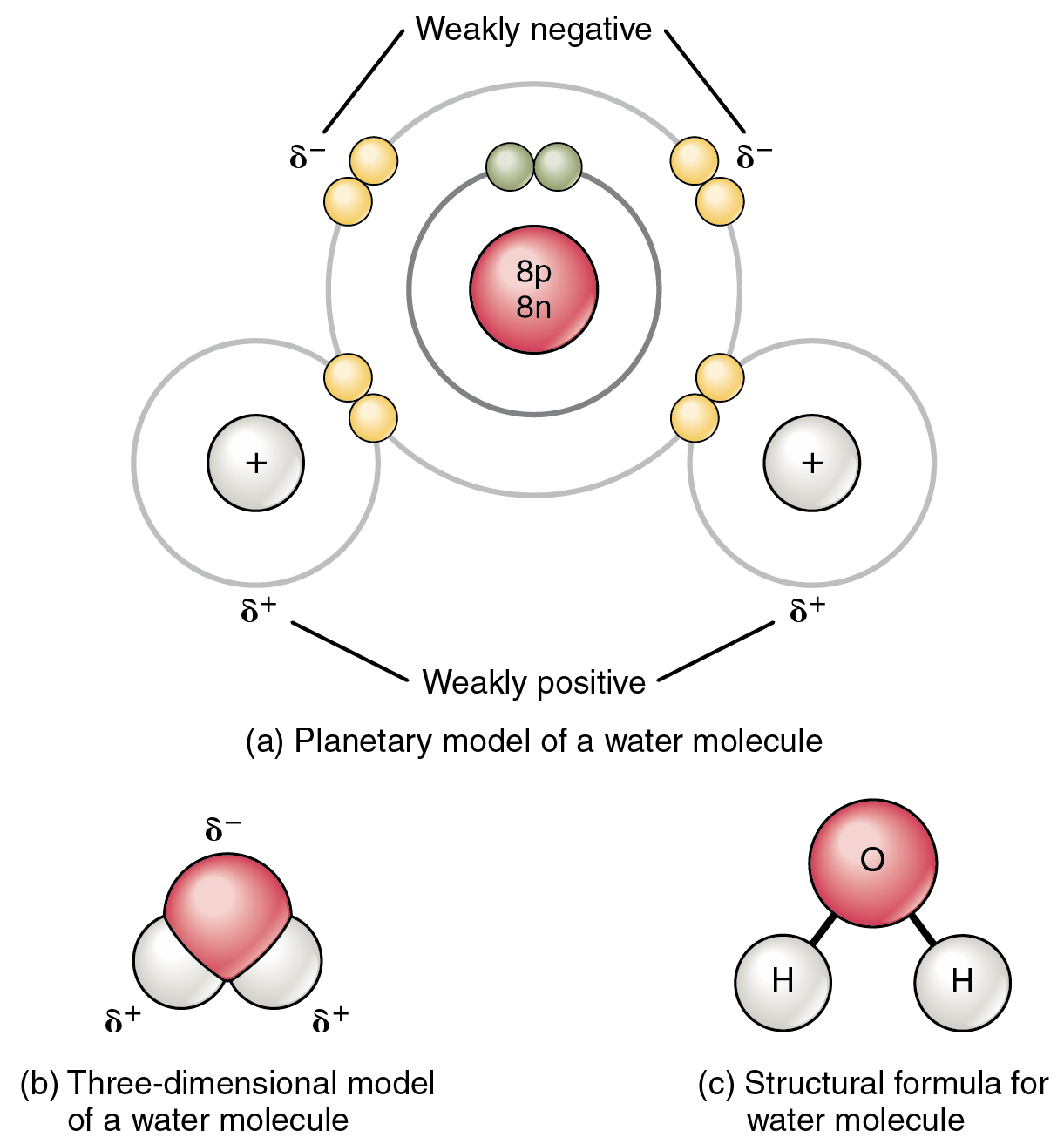
Attractive Forces and Bonds

Covalent Bond Biology Dictionary

The top panel in this figure shows two hydrogen atoms sharing two

Covalent Bond Examples Several Examples of Covalent (molecular) Bonds

CH150 Chapter 4 Covalent Bonds and Molecular Compounds Chemistry

PPT Covalent Bonds PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6647183

Chapter 5.6 Properties of Polar Covalent Bonds Chemistry LibreTexts
The Pair Of Electrons Participating In This Type Of Bonding Is Called A.
The Valence Of A Given Atom Is The Same In Most Stable Neutral Organic Compounds.
The Number Of Bonds An Element Forms In A Covalent Compound Is Determined By The.
For Example, Beryllium Can Form Two Covalent Bonds, Resulting In Only Four Electrons In Its Valence Shell:
Related Post: